COVID-19 is driving the increasing need for lung transplants in the US
The need for lung transplants in the United States has risen due to COVID-19, with 10% of all lung transplants now needed to treat those affected by the virus.
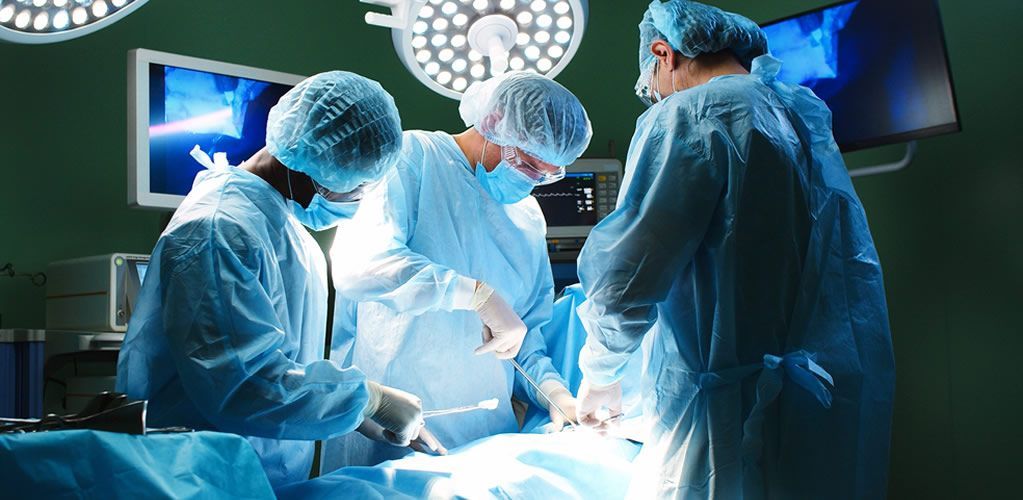
The need for lung transplants in the United States has risen due to COVID-19, with 10% of all lung transplants now needed to treat those affected by the virus.
C OVID-19 is causing an increasing need for lung transplants in the United States. According to data from the United Network for Organ Transplants (UNOS), one in 10 of all lung transplants are now required to treat patients impacted by the virus.
Dr Selim M. Arcasoy, Medical Program Director of the Lung Transplant Program at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia, stated that those who contract COVID-19 may develop very severe pneumonia, leading them to require either high flow oxygen support or even mechanical ventilator and extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO) support. He noted that some of these patients recover partially, but if they remain stuck with pulmonary fibrosis – resulting in chronic hypoxemic respiratory failure – they become candidates for a transplant.
CONTINUE READING...
Enjoy unlimited access now.
To get full access to this article,
simply become a member of PUBLIC SQUARE now.
By doing so, you will be supporting
our independent journalism.
MEMBERSHIP OPTIONS:
£3/month ∙ £5/month ∙ £7/month
You can cancel anytime.
BECOME A MEMBER
Already a member? Sign in here!
BENEFITS OF MEMBERSHIP:
✅ Read exclusive member-only articles
✅ Read our daily review of the UK front pages
✅ Receive every new article by email
✅ Access all our articles
✅ Get Special Discounts with our partners
✅ Join the conversation: Comment our articles
✅ Access our archives
✅ More importantly: Support independent journalism and keep the magazine going
Read more

— A global report reveals rising repression and criminalisation of climate and environmental protests, with state and corporate actors employing anti-protest laws, harsher policing, and violence to stifle activism worldwide.

— Polling accuracy in the U.S. presidential election faced criticism, despite improved performance over 2020. Small errors in a tight race amplified perceived inaccuracies, but swing state polls generally proved reliable, reflecting a close contest, Professor John Curtice explains.

— National populism, fuelled by media-backed disinformation, anti-immigrant rhetoric, and libertarian ideologies, threatens democracies globally by eroding institutions, fostering fear, and exploiting divisions.

— A UK tribunal upheld the ban on a Chinese businessman, citing national security risks. His links to Prince Andrew underscore concerns about foreign influence and lapses in public scrutiny.
|
|

